What is ethernet cable or LAN cable? Most consumers want to know about this query. It is not a hidden truth that wired cables are in high demand when there is a need for fast internet access. But there are some myths and details that you should know about your networking cables. Like cat5e, cat6, and Cat6a difference.
In this guide let’s sort out the complications of the ethernet cables and explain the general ethernet cable vs shielded ethernet cables, ethernet cable wiring, wiring a network cable, and ethernet cable color order. So stay on this blog to know better.
Must Read: Which Connection is Right for You? Ethernet vs. WiFi Showdown
What Is An Ethernet Cable?
In simple words, the LAN cable is the protocol for connecting various devices to support all the devices’ commands and functions. It has become the need for every small business to large enterprises to get speed as compared to their network equipment. Every business needs active Internet access throughout its business operations.
Ethernet cables are considered the backbone of the network setups, giving out high speed, bandwidth, and performance no matter whether we have access to wireless (WiFi) technology. It is highly secured and has a long lifespan. So you do not need to worry about poor performance or slow speed.
Ethernet Cable Categories
Cat1 up to Cat5 cables are obsolete so here we are talking about the primary gigabit cable Cat5e and the modern Cat cable (Cat6 cable and Cat6a Cable). The need for improvising the cable speed or bringing on the next advancement in cable technology is due to the high server speeds that are mostly needed for commercial and industrial applications.
The LAN cables are selected with the server specs and it will give you joy regarding the functionality of the network speed. For that, you need to know the ethernet cable categories and their intent.
- Enhanced Category 5 Cable (Cat5e)
- Category 6 Cable
- Augmented Category 6 Cable (Cat6a)
These are the top most advanced ethernet cables but besides this Cat7 and Cat8 cables also play an important role in the market. The only reason these cables are not frequently used in residential is their shielded behavior and these cables are designed the offer maximum protection as these are tightly shielded and used for longer transmission for sending bulk data or information in multiple buildings.
External Structure Of Ethernet Cables
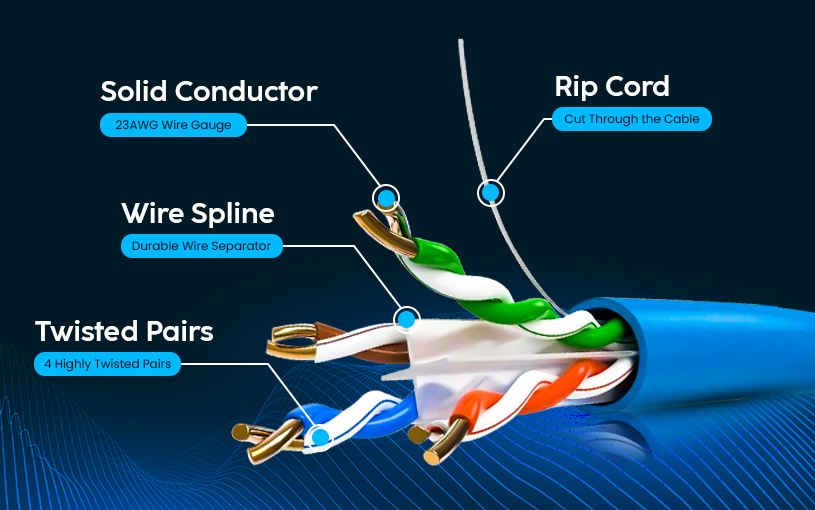
Peel any jacket of the ethernet cable you will just see a simple structure of 8 individual conductors that are twisted according to the ethernet cable’s conductor color order. But if you look more closely you will see the twist per inch will increase if you proceed with the cable category.
The twist in the cable helps in fighting and making the signals intact so there are no chances that the magnetic field generated when current is passing through the cable will overlap to outside signals causing interference in the cables normally known as “Crosstalk”. The Twist in the Cat6 cable is 4-5 twists per inch but in the Cat6a cable it is observed 6-7 twists per inch which is why Cat6a shows better crosstalk values than cat6 but both are supreme in their functioning.
The color of the cable’s conductor will determine the wiring scheme which we will discuss in detail separately. After the conductor, there comes a spline in the Cat6 plenum or riser cable the spline is the cross skeleton as shown in the diagram is the plastic material but of very useful as it maintains the distance between 4 twisted pairs and reduces the pair-to-pair crosstalk. This is the next ultimate reason why you should buy cat6 or cat6a cable.
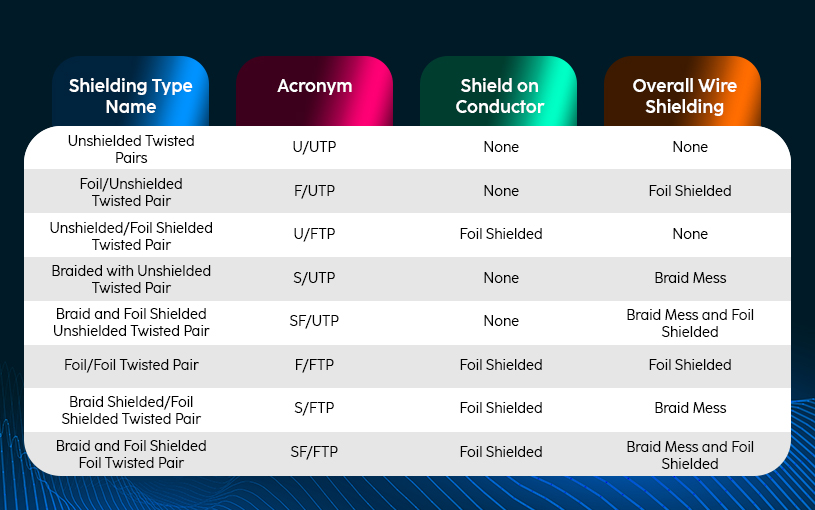
Shielded Vs Unshielded Cables Difference
This is the next important factor that you need to read and understand, the difference between Shielded and Unshielded network cables. What is the need? Why Shielded cables are more secure? Can shielded cables be used in residential setups? There are multiple frequently asked questions asked about Shielded cables. Let me guide you briefly.
The shielded cables are one step ahead of the general ethernet cables due to some reason. The reason cable comes in a shielded category is that STP cables have an additional insulation layer between the cable jacket that gives the cable more room to stand firmly against interference.
Likewise, Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a all have shielded variants, the shield present is of two types — Aluminum Foil and Braid Mess. Where Aluminum Foil is denoted by F and the Braid Mess is denoted by S. It is because you do not get confused in terms like U/FTP and S/UTP.
Now what do the shielding types mean? For that, the better and more appropriate manner is to draw a table for a clear understanding.
Shielding Cable Types
Ethernet Cable Wiring
This is the most common phenomenon when installing a cable you need to terminate the network cable before or after installation. The termination practice is mostly done after installation of the ethernet cable like Cat6 or Cat6a when properly installed at their specific destination.
The conductors of the Network Cable have 8 individual wires mostly observed in the following colors for ethernet cable wiring.
- Green and striped green or white green
- Brown and striped brown
- Blue and striped blue
- Orange and striped orange
These ethernet conductor color orders are to identify the termination wiring scheme for making a crossover cable or straight-through cable. The ethernet cable wiring schemes are of two types
1. T568A
2. T568B
For modern ethernet cables or equipment, T568B is likely to be used to get the right speed and it is done by following the color order as follows,
- White-Orange
- Orange
- White-Green
- Blue
- White-Blue
- Green
- White-Brown
- Brown
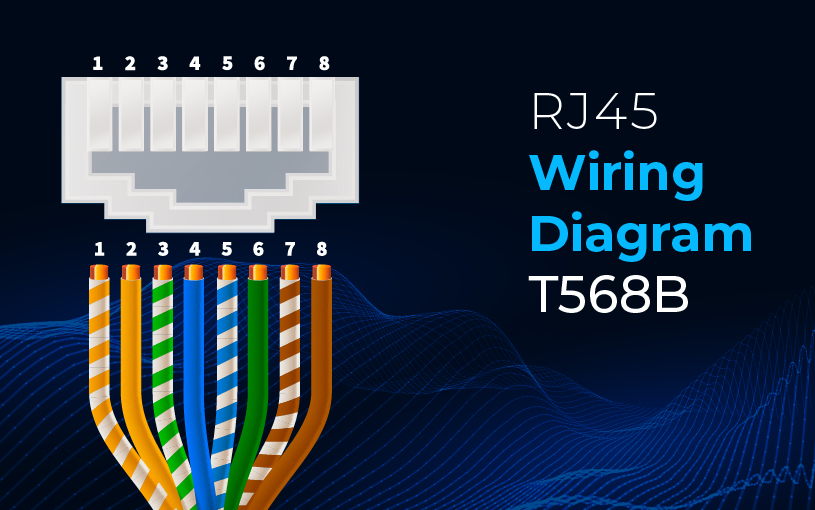
These are the color sequences that you should follow for both ends of the cable so that you will make the right type of cable termination to function properly. If you observe the same wiring standards as of T568A or T568B on both sides of the network cable the cable is known as straight-through cable. If you make an alternate connection wiring sequence like one side is terminated using T568A and the other end of the cable is T568B the cable is called crossover.
Now for the T568A termination process, the wiring schemes are as follows.
- White-Green
- Green
- White-Orange
- Blue
- White-Blue
- Orange
- White-Brown
- Brown

Ask about the cable installer which termination process is more precisely to fit your network cable.
Ethernet Cables Speed Ratings
LAN cables show different speed ratings if we compare all the ethernet categories. Understanding speed ratings for Cat5e, Cat6, and Cat6a is the most important factor for the buyers and also understanding the need for your server is dominant in selecting the right type of ethernet cable.
Starting with the Cat5e Network Cable, there are two types of conductors used for manufacturing the enhanced category 5 cable. The Cat5e cable bulk cable is made up of pure copper and CCA (Copper-Clad Aluminum). The Cat5e cable features a 24 AWG conductor size that is bound to deliver 350 MHz bandwidth speed.
For the speed, The Enhanced Category 5 cable gives out 1 Gbps speed at 50 meters (164ft) or 100 Mbps at 328ft (100 meters). Likewise, the speed is associated with the need to cater to server speed often adopted by your ISP (Internet Service Provider).

Then there comes a modern network cable Category 6 cable, the cable is a bit more advanced cable you can buy from the market or online. Similar to Cat5e the cable has two standards in the conductor — Copper and CCA, but what makes the difference is the 23 AWG that delivers the maximum bandwidth of 550 MHz. The internal structure is quite solid and the cable cancels the effects of outside interference (Crosstalk) which causes a delay in data transmission. Network cable speed for Cat6 at shorter lengths let’s say 50 meters is 1 Gbps and for longer lengths, this modern Cat6 cable delivers 10 Gbps speed for running high ethernet applications. This cable is good for PoE but in a copper conductor or bare copper.
For Cat6a cable, this Augmented Category 6 is only made up of Pure Copper Conductor and the diameter size is just the as same Cat6 23 AWG. The cable at shorter or longer lengths delivers a maximum of 10 Gbps speed with the highest bandwidth of 750 MHz. Therefore this cable is the ultimate solution for various commercial and industrial applications. The Cat6a cable in bulk eases the heavy installation.

What Does Ethernet Cable Look Like?
The ethernet cable looks just the same as the telephone cables but with more wires inside the cable. These wires allow data to pass through various devices. There are 4 twisted pairs and each pair is involved in Tx (Transmission) and Rx (Receiving) the signals to and fro. Ethernet cable comes in various sizes and colors like gray, black, blue, white, and green to adjust the color code of the buildings. The termination process of a network cable observes the RJ45 connector on both ends of the cable hence making it eligible for connecting the suitable devices.
How Do You Make An Ethernet Cable?
This is the most asked question regarding the LAN cable how to terminate an ethernet cable? Here is a brief explanation.
First, choose the cable category like Cat5e, Cat6, or Cat6a cable according to your choice.
Now you need the following accessories — scissors, crimping tool, cutter, cable tester, wire cutter. Now following are the steps that you will follow to make an ethernet cable workable.
- Cut a few meters extra of the required length of the cable, now on one side of the cable cut the cable jacket carefully.
- After cutting you will see the 4 twisted pairs, make them apart and straight, and follow the color code you want for your termination process. T568A and T568B.
- Align all the wires according to the wiring scheme and cut them to make them equal.
- Now insert the wires into RJ45 connectors and push the wire gently using a crimping tool apply pressure to crimp the wires to the RJ45 connectors.
- Test the cable with a cable tester and repeat the process on the other end of the cable.
Final Thought
Ethernet cable itself is a broad range of technical wiring terminology that is only used for supporting many networking devices and also to deliver power and data transmission simultaneously PoE.
This whole summary will help you understand the definition of Networking Cables or LAN cables for your home, office, or corporate sectors to work efficiently and effectively. The right choice of ethernet cable may help you to get the maximum output in a single go without affecting your performance.
| Specification | Cat5e | Cat6 | Cat6a |
| Cable Jacket | Plenum, Riser & PVC | Plenum, Riser & PVC | Plenum & Riser |
| Wire Gauge | 24-AWG | 23-AWG | 23-AWG Highly Twisted |
| Frequencies | 350 MHZ | 550 MHZ | 750 MHZ |
| Installation Temp | 0°C to 60°C | 0°C to 60°C | 0°C to 60°C |
| Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs |
| Package | Easy Pull Box | Easy Pull Box | Wood Spool |
| Colors | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow |
| Standard Compliance | ETL, FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS | FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS | ETL, FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS |




