
You surely heard the phrase “Why My WiFi Connection Is Slow?” the most spoken phrase of wireless connection (WiFi) users. Is Ethernet Faster Than WiFi? There is a complex debate about knowing the terms and the sound knowledge to update you regarding the speed and the other factors that might be the reason to affect the speed of ethernet vs WiFi.
You might need some sort of information that will help you identify the difference between Ethernet vs WiFi. There are two possible ways that you get online access through wired cable “Ethernet” or wireless connection “WiFi”. But are you confused about which works faster? Yes, it’s an ethernet vs WiFi debate let’s see who is the winner.
In this blog, we are going to start with the ethernet, the wired giant for networking. Here it is.

What Is An Ethernet?
You are quite familiar with the names Cat5E, Cat6, and Cat6a; these are known as Ethernet cables. Whereas, Ethernet is a protocol that is used to connect devices in a WAN (Wide Area Network) or LAN (Local Area Network). It can share information with other hardware devices such as computers, gaming consoles, hubs, internet routers, etc. The ethernet has some key aspects that are as follows;
- It creates a physical connection between devices whereas WiFi uses radio waves for transferring data.
- Stability – Ethernet is more stable than WiFi connection due to some factors.
- Speed – Ethernet can support significantly faster speed and transfer rates than WiFi for example Cat6 and Cat6a cables are the best examples.
- Security – Wired cables are considered a more reliable and secure connection as they cannot be easily intercepted by unauthorized devices
Components
If we talk about the ethernet network it contains the following components just like
- Ethernet Cables — category cables that are the source of transmitting information.
- Ethernet Ports — there are ethernet ports known as female ports that connect RJ45 connectors to transfer the commands.
- Network Switch — it works as a central hub creating a bridge with multiple devices to connect and communicate efficiently.
Applications
Ethernet applications are widely used in various situations like
- Home Networks
- Office Networks
- Data Centers
In simple words, the definition of ethernet is the primary technology for wired networking that offers a valid, secure, and high data speed connection for various and particular applications.

What Is WiFi?
WiFi stands for “Wireless Fidelity” and is a device that uses wireless signals “Radio Waves” to connect or provide internet access to particular devices like laptops, computers, tablets, etc. The best part of WiFi is the movability and there is no need for physical cables thus very convenient. Likewise, ethernet some of the key features are also associated with WiFi that are;
Features
- Wireless Connectivity – no physical wires
- Scalability – can connect multiple devices
- Security – offer WPA2 encryption for protection
- Convenience – more easy setup than ethernet
Components
No wonder WiFi also has some of the main components required for working and dictates the functions it can accommodate.
- Wireless Router – connects to your ISP using a wired connection.
- Wireless Access Points – can extend your range of WiFi networks and can connect to another by proper configuration settings.
- Wireless Adapters – previously installed in computers, or laptops to access the wireless connections.
In the real world WiFi is a wireless networking device that is available in every house and office to connect multiple devices to provide a flexible mode of communication and working environment. Understanding the key features may be valuable in the future to idealize Ethernet vs WiFi connection.
How WiFi Works
Here you will find how WiFi works and what are the characteristics that are necessary to add on during its working.
- Data Transfer
- It converts data when you command to another device printer or email.
- Wireless Router
- By using frequencies ranging from 2.4 GHz to 5 GHz they are further converted into radio waves.
- Wireless Signal Transmission
- Radio waves simply travel from the antennas carrying information to the other device.
- Device Reception
- Once the device recognizes the information from the radio waves, it further converts it to digital packets
- Data Access
- It potentially works while sending emails, transferring files, downloading the file, etc.
Factors to Consider: Ethernet vs Wifi
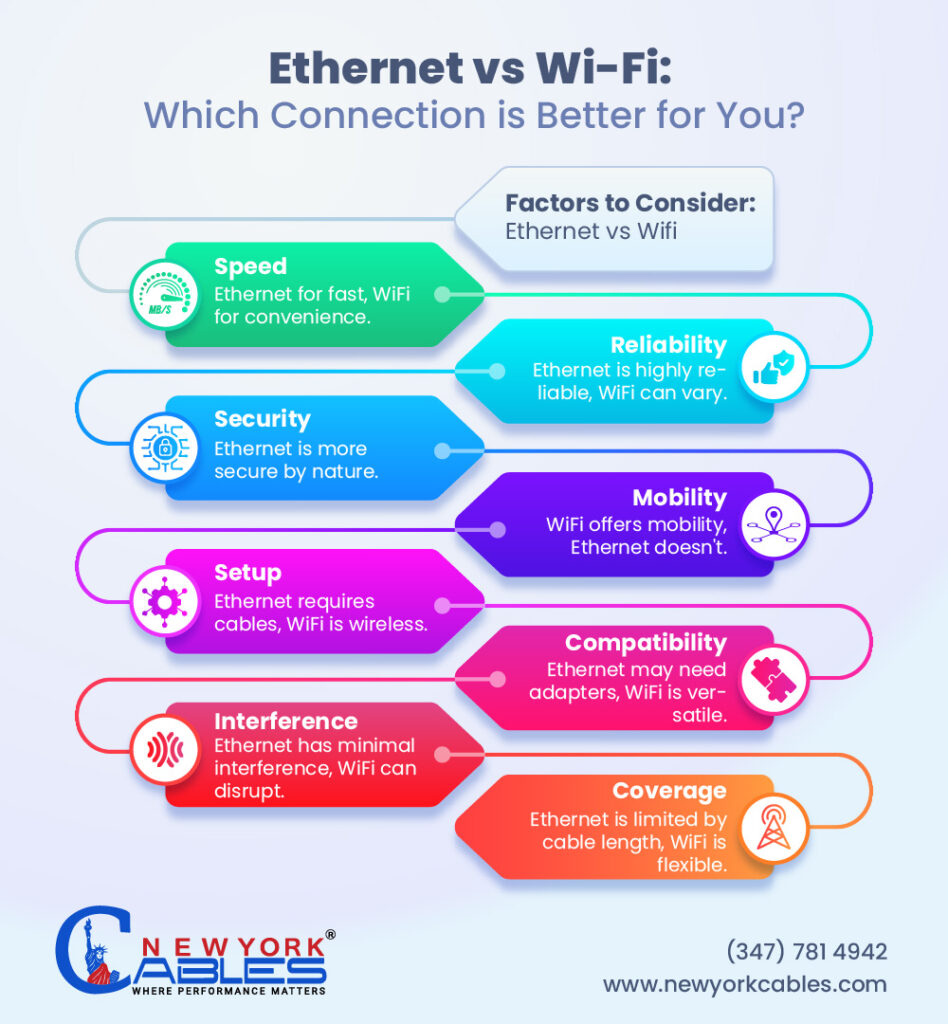
Ethernet Vs WiFi — Who Is The Winner?
The wired cables are the king of networking and no one can replace their existence and cannot deny their adaptability for providing the speed potential. But as wireless technology is introduced we must think about what is more suitable for clear understanding. So without taking much of your time let’s find the key difference between Ethernet and WiFi.
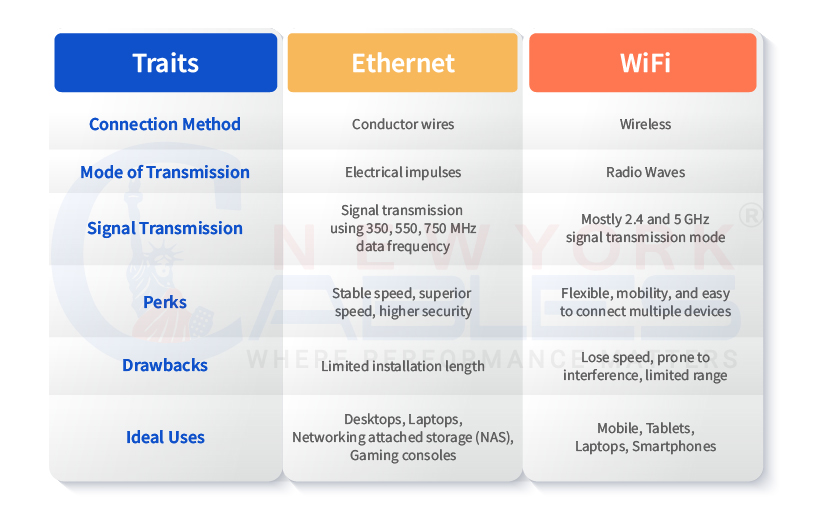
The above difference is precise and is ideal for developing the sense that wired cables are more convenient, long-lasting, and less prone to interference. Whereas the WiFi is the device that is installed, and its signals get weak when more devices are connected, placed behind the wall, or furniture is placed on the second floor, etc.
Now you are clear about the ethernet and WiFi specs let’s split the information and come to the Frequently asked questions that are more engaging and require a solution.
Must Read: Ultimate Guide to LAN vs WAN Networks
Is Ethernet Faster Than WiFi?
It’s a Yes, the ethernet is always faster than wifi and will always be due to the reason that ethernet cable speed caters to a single piece of equipment. Whereas, WiFi connects multiple devices at the same time so its speed may fluctuate and when you need a proper speed for playing online games you may get a high ping or latency rate which will result in a lag in the game.
The Wired Warrior — Ethernet
Whenever you need fast networking wired cables are the best heroes to fight for the cause to provide you with the potential ethernet cable speed at its best. But what is the reason that ethernet is compared to the speed of WiFi? Here it is to know which is better for networking needs. Let’s dig down a bit deeper in the discussion to unfold some facts about the ethernet cable speed.
- Physical Connection
- Dedicated Pathway — when connecting the ethernet cable there is no third party involved while connecting the cable hence it makes direct contact with the devices. The terminated cable then passes the electrical signals to the devices through the cable hence offering a dedicated pathway.
- Radio Waves Vs. Electricity — electricity needs a medium to travel and that medium is the copper conductors that are inside the ethernet cable, there are twists in the cable’s conductor so that the passing current less interferes with the outside signals. On the other hand, WiFi uses radio waves for the transmission of data but without a medium, the waves can be intercepted at any point which means they are more susceptible to interference. If more than one WiFi operates at the same frequency it will distort signal integrity making you lose connection.
- Higher Bandwidth Capacity
- Cable Categories — this is a known fact that each of the categories of the ethernet cable (Cat5E, Cat6, and Cat6A) has varying speeds and maximum bandwidth that set the cable apart from other cables. The definition of ethernet cable bandwidth is the amount of data traveled at a given time. Higher category cables like Cat6a LAN cable and Cat6a can handle significantly more bandwidth compared to standard WiFi.
- Gigabit Vs. Megabit — there are two sets of ethernet speeds (Fast Ethernet/100 Mbps) and (Gigabit Ethernet/1000 Mbps). The ethernet can handle 100 Mbps to 10 Gbps speed and it only caters to a single device. Hence there will be no speed sharing. But WiFi speed is measured in Megabits (Mbps) thus making a significant difference in data transmission.
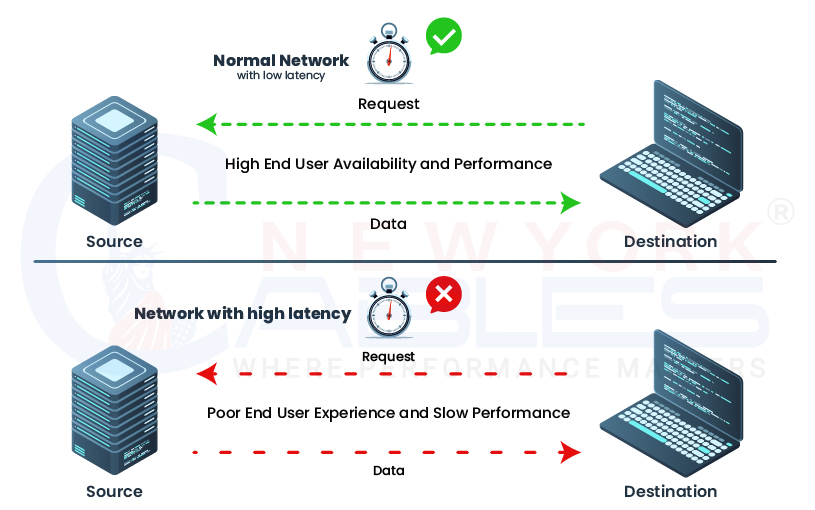
- Reduced Latency
- The latency rate is defined as the time data takes to travel between two points on a network. WiFi devices have high latency rates as compared to wired cables. So that is why data travels faster in wired cables than that of WiFi as it experiences some delay in transmission. Lower latency is not a good sign for online gaming, video conferencing, and real-time data transfer.
- Consistent Speeds
- Unaffected by Interference — using physical cable means that the connection cannot be influenced easily by external interference or factors that may bring down the performance of the cable. But moving away from the WiFi signal ranges your speed and the signals will fall.
- Fluctuations In WiFi — It depends on the location of the router, signal interference, and the number of devices connected to the WiFi. These signal fluctuations are so frustrating when you require a steady and reliable signal.
The above points for Ethernet vs WiFi clearly state that the ethernet is a winner and it can be a useful addition then a WiFi. The following physical connection, higher bandwidth, lower latency, and consistent speed define it superhero when transferring data and comparing speed with WiFi.
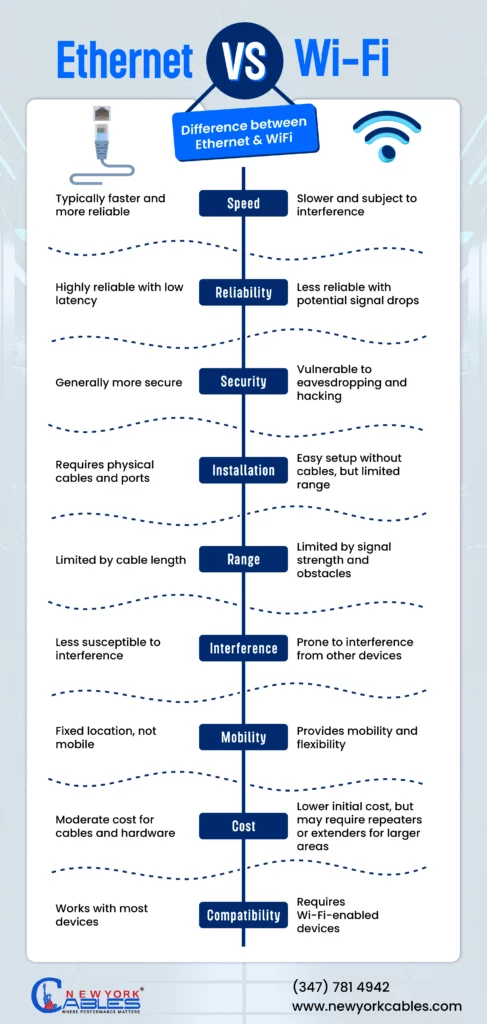
WiFi Standards
Wireless technology has some standards that define its speed and other specs. Just like modern ethernet cables like Cat6 and Cat6a can support 10G, there are some speed limitations that we see in WiFi as set by IEEE.
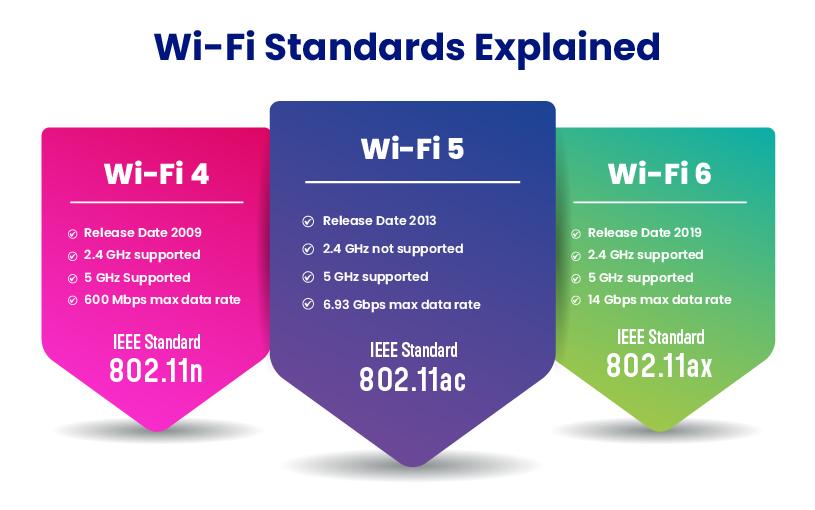
These are the speed standards for WiFi and here you can see clearly that the WiFi 4 upon connecting to multiple devices will fall short of transferring data and the rest of the devices. It also supports 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz while 5 GHz is more efficient than 2.4 GHz ethernet.
Must Read: Coax vs Ethernet Cable: What’s The Difference?
WiFi Vs Ethernet Gaming
WiFi vs Ethernet for gaming this phrase is mostly heard by hardcore gamers or those who used to stream online games on YouTube or social media channels. Gaming is a kind of activity for many adults and children whether to challenge the opponent or to play one on one. But the main thing to focus on for online gaming is whether WiFi or Ethernet is suitable. Let’s find out using the following factors that can cause delays in online gaming.
One thing you all know for convenient online gaming speed and performance do matter. While WiFi gives you convenience, ethernet cords give out better performance regarding the speed and the bandwidth without any delay or compromise. Here is the breakdown for you to choose which is better for you for online gaming.
The Convenience Champion
- Untethered Freedom — WiFi connection makes you connect and move freely with your portable gaming device or with your laptop, if you are gaming on the Xbox or PS5 then take care that there are fewer hurdles between the WiFi devices.
- Easy Setup — the WiFi is protected by a WPA2 passcode that you set to encrypt the data and also prevent it from being used illegally. Just simply select the name of the wireless device and easily connect to your console. There is no such need for cable configurations.
The Performance Powerhouse — Ethernet
- Blazing-Fast Speed — compared to WiFi the ethernet cables send millions of packets of data at longer lengths. Less distortion and minimum interference translate to smooth gaming.
- Lower Latency — It is considered to be the game killer and not a good sign for every gamer who is streaming its gameplay to social channels. Ethernet cable minimizes the latency rate and provides the best output to the gaming thus quick response.
- Unwavering Consistency — the twisted pair cables are less susceptible to EMI or RFI data interference, but ethernet cables are installed inside the home in horizontal and vertical spaces of the house and still possess the best results for gaming.
The ethernet often acts as a powerhouse by delivering the stable speed because while gaming response is all that you need a single delay can frustrate the gamer. The above discussion dictates the positive points of WiFi vs Ethernet gaming now just understand some drawbacks of both WiFi and Ethernet.
Drawbacks Of WiFi
- Slower Speed and Fluctuations — The speed of WiFi is significantly slower than wired (Ethernet) especially when you are using the older WiFi standards or if your WiFi catches interference from other devices. This pause can cause lag and stuttering during online gaming.
- Higher Latency — One of the major issues that make you scream “Why My WiFi Is Slow” is the high latency rates of the WiFi. It does so by the bulk user connected at the same time, and when you need speed for fast-paced games the higher latency slows down the reaction time.
- Security Concerns — Wireless devices have issues that before gaming you need to implement strong encryption (Security) to protect your data to connect by other devices. The WiFi standards may be older but once they are connected with more than 5 devices or more the speed splits up.
Drawbacks Of Ethernet
Just like WiFi ethernet has also some drawbacks that you need to consider before opting for the right one. Here are fewer points;
- Limited Mobility — Many gamers are fond of playing games while lying on the couch or bed but with Ethernet, you are tethered to the router with a wire and this will restrict the movement during gameplay.
- Installation — The ethernet cord needs to be installed at your house before you plug it into the gaming console. The cable needs to run through your walls or along baseboards which is a time-consuming process and aesthetically less pleasing for some users.
The Final Verdict — Ethernet Wins, But WiFi…
Many gamers earn by uploading gaming videos to their YouTube channels and those have come in the category of hardcore gamers. For serious gamers who need performance, and a competitive edge let me tell you “The Ethernet Is The Winner” not just by choice but by specifications. The war between “WiFi vs Ethernet Gaming” ends as the ethernet ensures unmatched speed, consistency, and lag-free data transmission for smooth gaming.
However, WiFi is not a loser, it is a runner-up that still supports the specs of some of the users who need to connect for wireless gaming and are fond of moving here and there while playing games, just like kids. It does so by prioritizing the needs and speed of complex gaming. If you are playing action games that need stable speed without any delay consider the ethernet your best pal.
All In One
The debate on Ethernet vs WiFi comes to an end where you can easily see that the ethernet is far ahead then the WiFi due to many reasons. The main reason is that the ethernet has a medium “Conductor” that allows the transfer of bulk information and makes it less deviated where performance is the key point.
Similarly, WiFi vs Ethernet gaming depicts that it is more convenient to use WiFi but for stable results and speed, ethernet is the best. This blog explains the key features of WiFi and Ethernet. Just to look more precisely at the need for your choice. If you are an occasional gamer use WiFi but if you are a regular gamer use ethernet and try its authenticity.
| Specification | Cat5e | Cat6 | Cat6a |
| Cable Jacket | Plenum, Riser & PVC | Plenum, Riser & PVC | Plenum & Riser |
| Wire Gauge | 24-AWG | 23-AWG | 23-AWG Highly Twisted |
| Frequencies | 350 MHZ | 550 MHZ | 750 MHZ |
| Installation Temp | 0°C to 60°C | 0°C to 60°C | 0°C to 60°C |
| Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs | 4 Twisted Pairs |
| Package | Easy Pull Box | Easy Pull Box | Wood Spool |
| Colors | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow | Black, Blue, White, Red, Green, Yellow |
| Standard Compliance | ETL, FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS | FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS | ETL, FCC, CE, CSA, ISO/IES, RoHS |




